User:Wavejava/testWikitext Source: en.wikipedia.org/wiki/User:Wavejava/testWikitext
Chinese
[edit]
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wavejava/testWikitext | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese | 北京 | ||||||
| Postal | Peking | ||||||
| |||||||
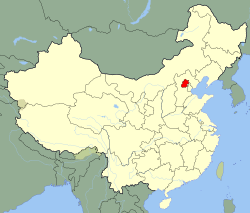
ⓘ (/beɪˈdʒɪŋ/ or /beɪˈʒɪŋ/ in English; Chinese: 北京; pinyin: Běijīng; IPA: [pèitɕíŋ]; Wade-Giles: Peiching or Pei-ching) (also formerly known in English as Peking (/piːˈkɪŋ/ⓘ or /peɪˈkɪŋ/)) is a metropolis in northern China and the capital of the People's Republic of China. It is one of the four municipalities of the PRC, which are equivalent to provinces in China's administrative structure. The municipality of Beijing borders Hebei Province to the north, west, south, and for a small section in the east, and Tianjin Municipality to the southeast.[6] Beijing is one of the Four Great Ancient Capitals of China.[7]
Beijing is China's second largest city, after Shanghai.[8] Beijing is a major transportation hub, with dozens of railways, roads and motorways passing through the city. It is also the focal point of many international flights to China. Beijing is recognised as the political, educational, and cultural center of the People's Republic of China,[8] while Shanghai and Hong Kong predominate in economic fields.[9][10][11] The city hosted the 2008 Olympic Games.
Few cities in the world besides Beijing have served as the political and cultural centre of an area as immense as China for so long.[12] The Encyclopædia Britannica describes it as, "One of the world's great cities,"[13] and declares that the city has been an integral part of China’s history for centuries, and there is scarcely a major building of any age in Beijing that doesn't have at least some national historical significance.[12] Beijing is renowned for its opulent palaces, temples, and huge stone walls and gates.[14] Its art treasures and universities have long made the city a centre of culture and art in China.[14]
Pronouce
[edit]English pronouce :
/pèitɕíŋ/: {{IPA|en|pèitɕíŋ|}} -> IPA: /pèitɕíŋ/
/beɪˈdʒɪŋ/: {{pron-en|beɪˈdʒɪŋ}} -> pronounced /beɪˈdʒɪŋ/
/beɪˈdʒɪŋ/: {{pron-en|beɪˈdʒɪŋ}} -> pronounced /beɪˈdʒɪŋ/
/beɪˈʒɪŋ/: {{IPA|en|beɪˈʒɪŋ|}} -> /beɪˈʒɪŋ/
Foreign pronouce :
[pèitɕíŋ]: {{IPA|und|pèitɕíŋ|}} -> IPA: [pèitɕíŋ]
IPA: [pèitɕíŋ]: {{IPA2|pèitɕíŋ}} -> IPA: [pèitɕíŋ]
/beɪˈdʒɪŋ/: {{pronounced|beɪˈdʒɪŋ}} -> pronounced [beɪˈdʒɪŋ]
/beɪˈdʒɪŋ/: {{pronounced|beɪˈdʒɪŋ}} -> pronounced [beɪˈdʒɪŋ]
[beɪˈʒɪŋ]: {{IPA|und|beɪˈʒɪŋ|}} -> [beɪˈʒɪŋ]
Others
[edit]A♣
- ^ "Township divisions". the Official Website of the Beijing Government.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
exceeds 17was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
radiowas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
dailywas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
enwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "Basic Information". Beijing Municipal Bureau of Statistics. Retrieved 2008-02-09.
- ^ "Beijing airport beefs up security for Olympics". MSNBC. Associated Press. 2008-02-22. Retrieved 2008-03-15.
- ^ a b "Beijing". The Columbia Encyclopedia (6th edition ed.). 2007.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|edition=has extra text (help) - ^ "Hong Kong and Shanghai as Twin Engines for China's Economic Development, says TDC Executive Director". Hong Kong Trade Development Council. 1996-12-18. Retrieved 2008-10-03.
- ^ "Hong Kong and Shanghai vie to be China's financial center". International Herald Tribune. 2007-01-15. Retrieved 2008-10-03.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ "Hong Kong and Shanghai Duel for Financial Capital". New York Times. 2007-01-16. Retrieved 2008-10-03.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ a b "Beijing". Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Retrieved 2008-08-03.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ "Peking (Beijing)". Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 25 (15th edition, Macropædia ed.). p. 468.
- ^ a b ""Beijing"". World Book Encyclopedia. 2008. Retrieved 2008-08-07.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help)